Floating Point Units
This document explains the integration of floating-point units in Dynamatic. Dynamatic relies on external frameworks to generate efficient floating-point units. The current version of Dynamatic supports floating-point units from two generators:
How to Specify the Unit Generator?
In order to specify which units to use, the user can use the following command when executing dynamatic:
set-fp-units-generator generator_name
For instance, here is a complete script used in Dynamatic’s frontend that uses the floating-point units generated by Flopoco:
set-dynamatic-path .
set-fp-units-generator flopoco
set-src integration-test/fir/fir.c
compile
write-hdl
simulate
synthesize
exit
Dynamatic uses flopoco by default.
Important: Using Vivado’s Floating Point Units
Vivado’s floating point units are proprietary. Therefore, we need to compile the modelsim simulation library using Vivado, and point Dynamatic to the location of the simulation library and the installation path of Vivado.
Compiling Simulation Library for ModelSim
To use the floating point units provided by Vivado, we need to compile them using Vivado. In Vivado, select Tools -> Compile simulation libraries -> ModelSim simulator, and set the path to where your ModelSim is (see the screenshot below).
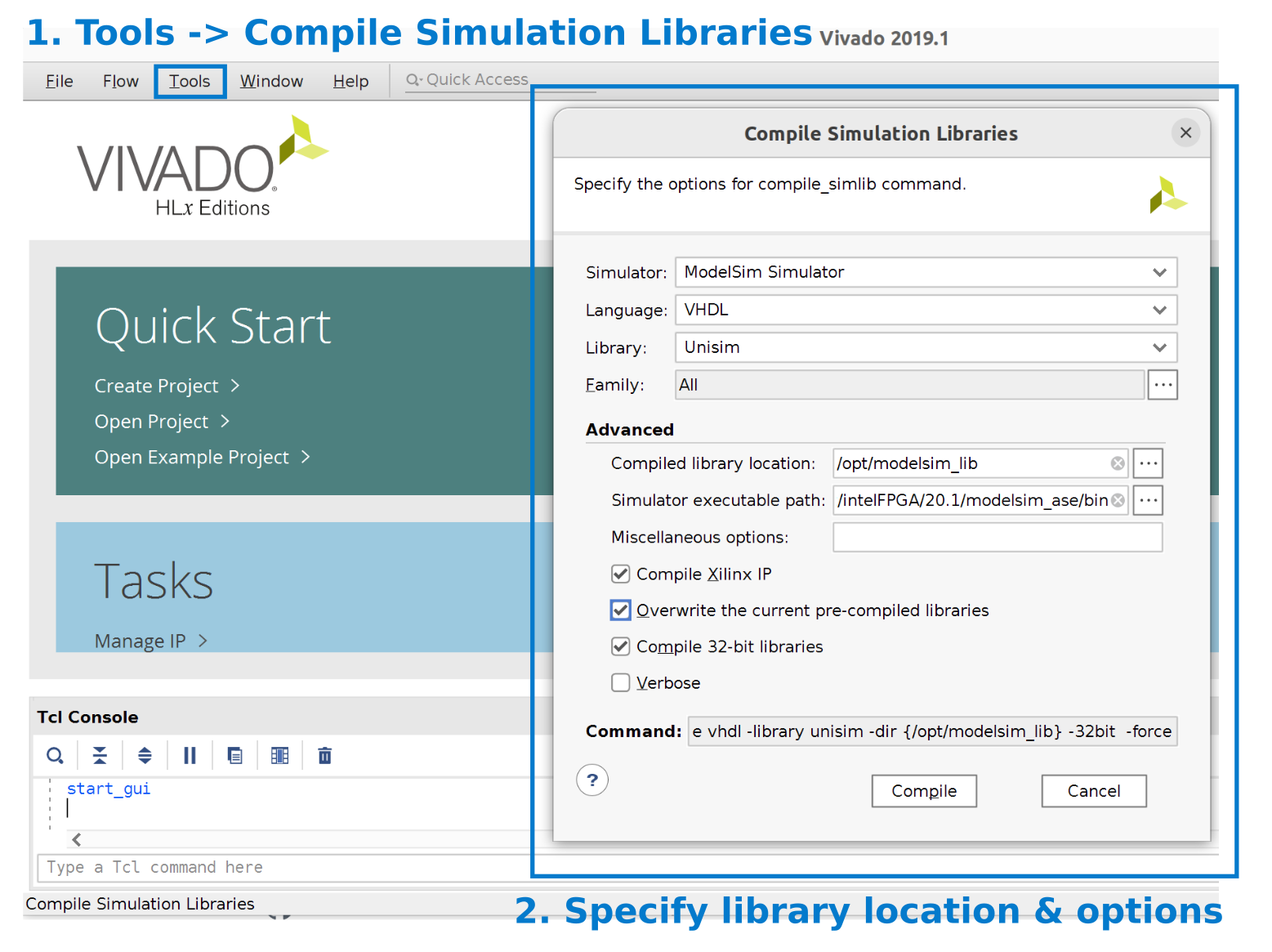
Please refer to this link for more information on how to compile the simulation library for ModelSim.
Make sure that you have compatible versions of Vivado and ModelSim. The following link contains a list of compatible versions: https://www.xilinx.com/support/answers/68324.html
Once the user has downloaded the Vivado IPs, the user has to update the path of these libraries for modelsim simulation by updating the path /opt/modelsim_lib/ in this modelsim.ini.
Important: Extra setup for Vivado
Additionally, the user has to provide the path to the Vivado installation folder using set-vivado-path. Here is a complete script for Dynamatic’s frontend:
set-dynamatic-path .
# Installation path of Vivado
set-vivado-path /path/to/vivado/Vivado/2019.1
set-fp-units-generator flopoco
set-src integration-test/fir/fir.c
compile
write-hdl
simulate
synthesize
exit
The default value for the vivado path is /tools/Xilinx/Vivado/2019.1/. This information is essentially to correctly integrate necessary simulation files of Vivado.
RTL and Timing Information
This section describes the organization of RTL modules and the delay/latency information of the floating point units inside Dynamatic.
Dynamatic wraps the floating-point IPs with handshaking logic. Currently, the IP cores are extracted and wrapped in handshake wrappers offline, and we save them in:
# Handshake units with flopoco IP cores:
data/vhdl/arith/flopoco/*.vhd
# Handshake units with Vivado IP cores:
data/vhdl/arith/vivado/*.vhd
The same applies to the Verilog backend where the paths are data/verilog/arith/flopoco/*.vhd and data/verilog/arith/flopoco/*.vhd, respectively.
Internally, Dynamatic uses two sets of files to track how they are generated and the delay/latency properties of them:
- Units with Flopoco IP cores: rtl-config-vhdl-flopoco.json (for RTL generation) and components-flopoco.json (for retreiving the delay/latency values).
- Unist with Vivado IP cores: rtl-config-vhdl-vivado.json (for RTL generation) and components-vivado.json (for retrieving the delay/latency values).
For more information related to timing information, please refer to this markdown.
IMPORTANT: Flopoco does not currently generate Verilog code. When the Flopoco FPU units are specified, the Verilog backend uses VHDL file which have been modified to adapt to Verilog. Hence, there is a mixed-language (VHDL and Verilog) generation.
IMPORTANT: The files used for simulation of the Vivado IPs are specified in VHDL for Modelsim. Hence, when simulating the Verilog modules, the core IP function is specified in VHDL. Hence, there is a mixed-language (VHDL and Verilog) simulation.
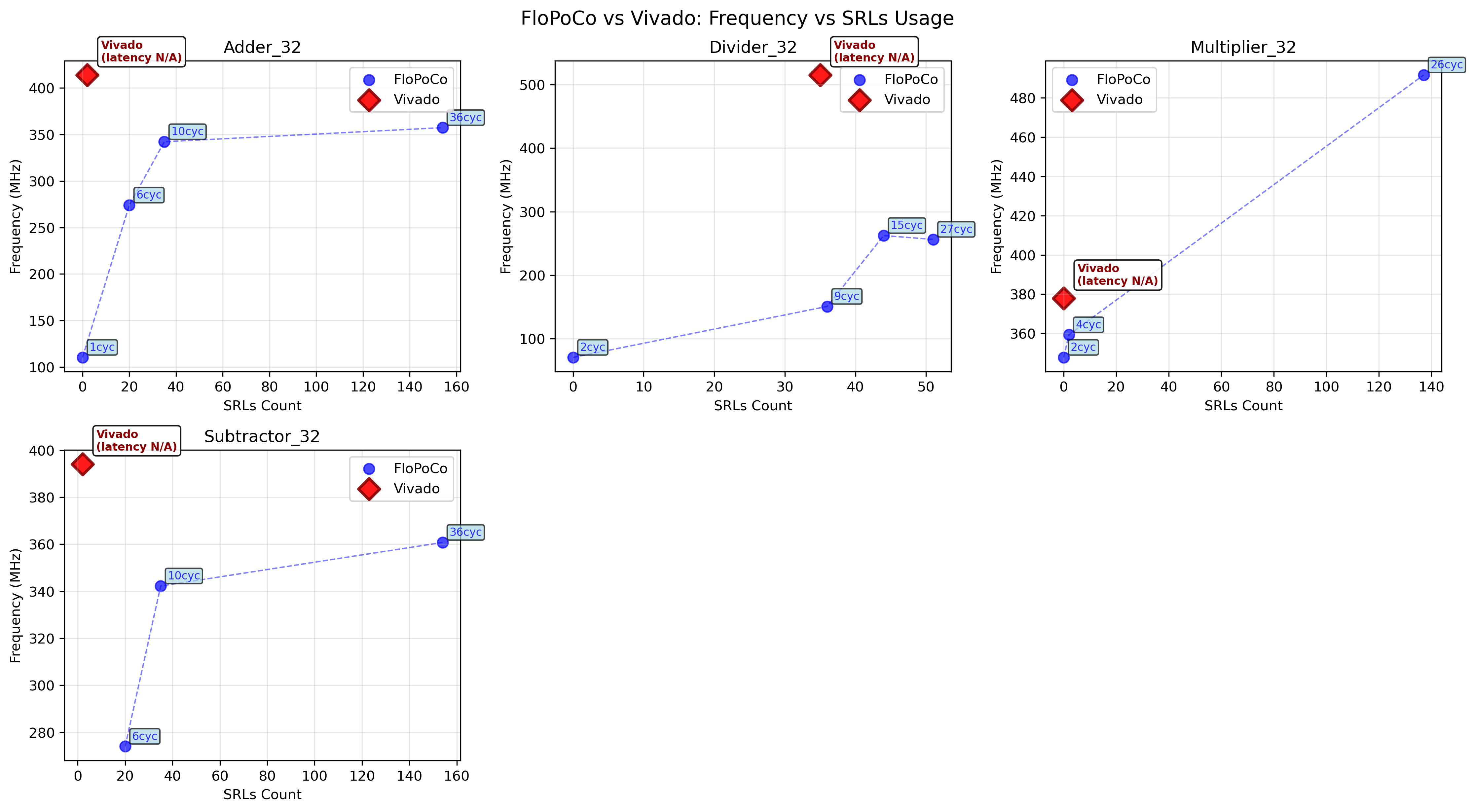
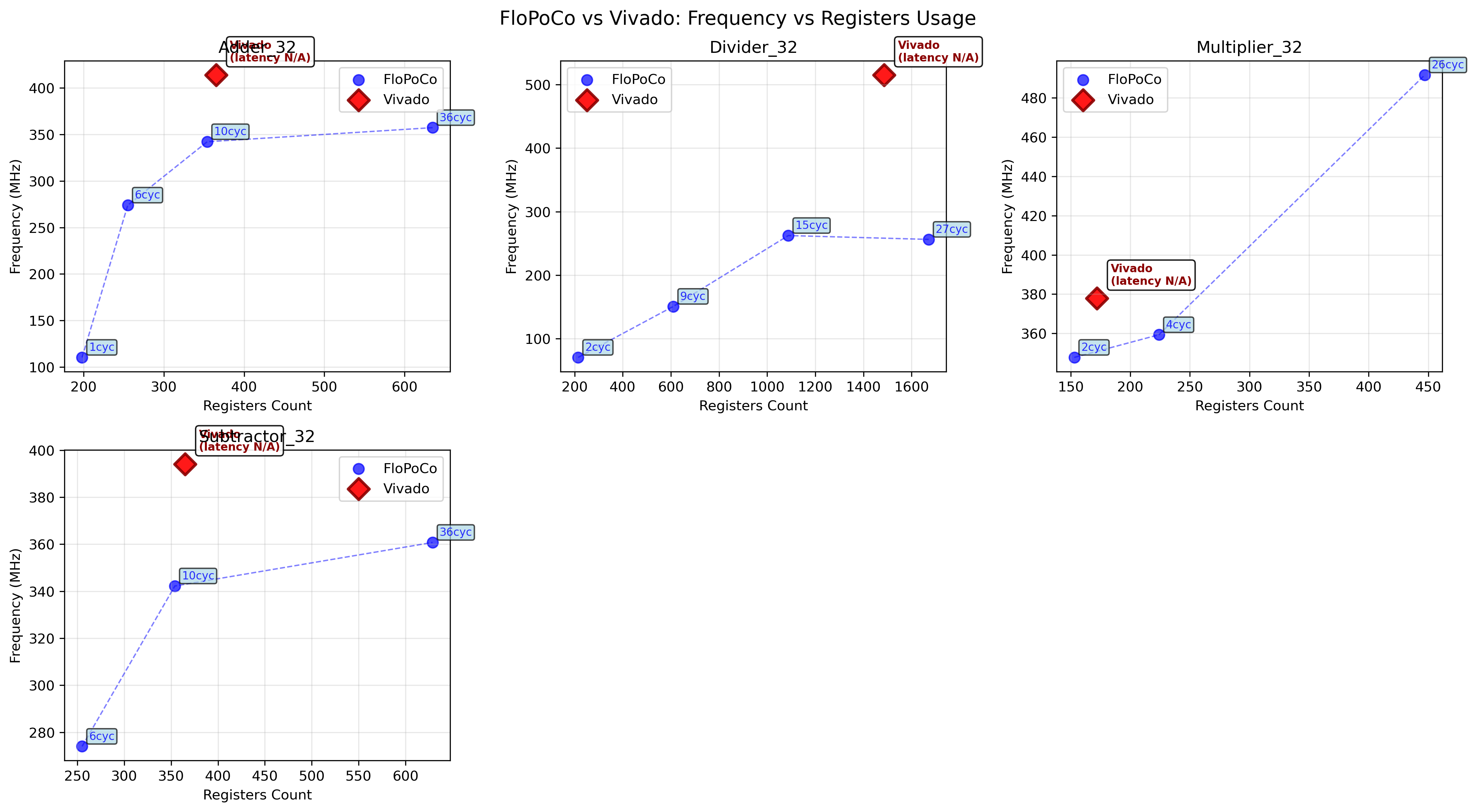
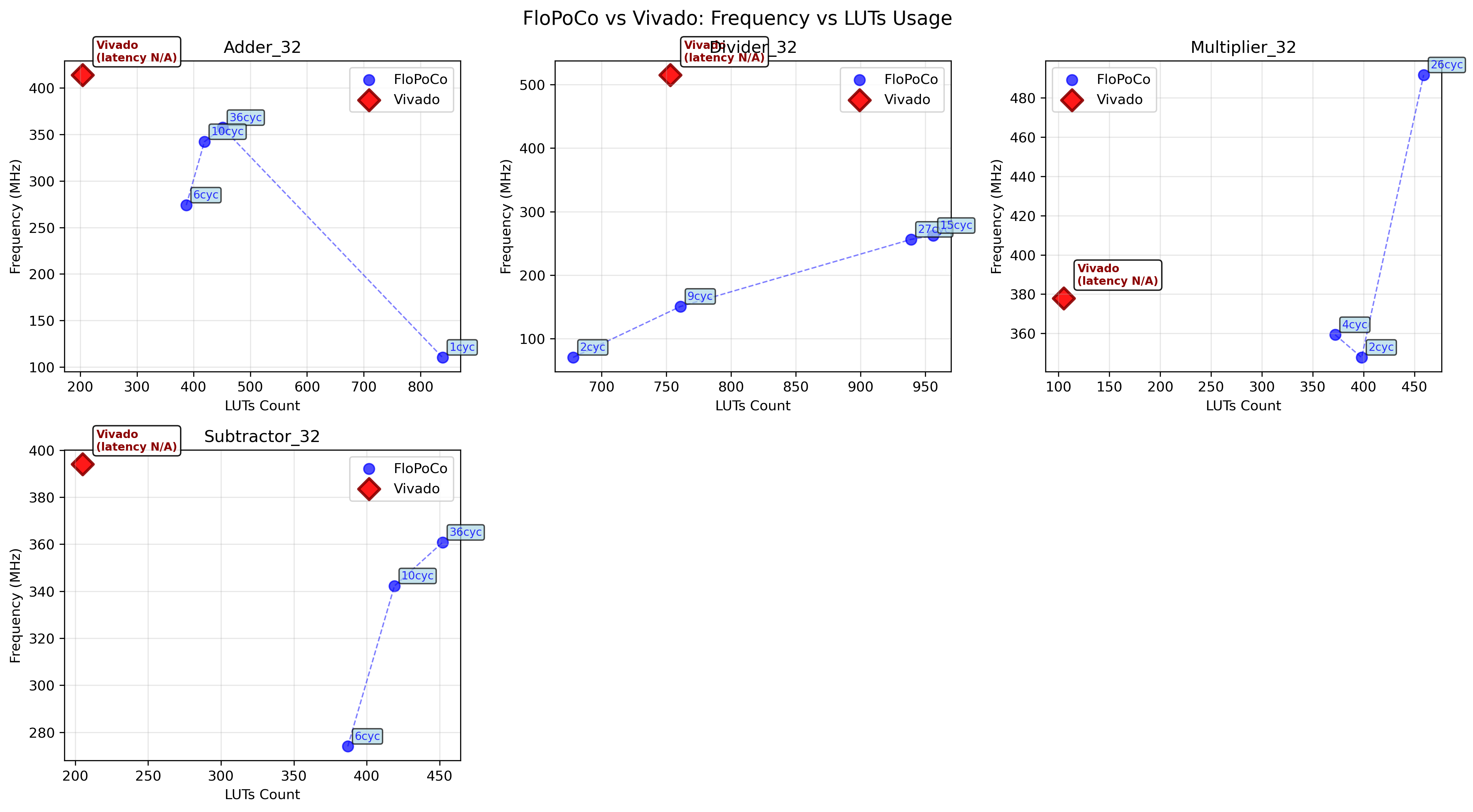
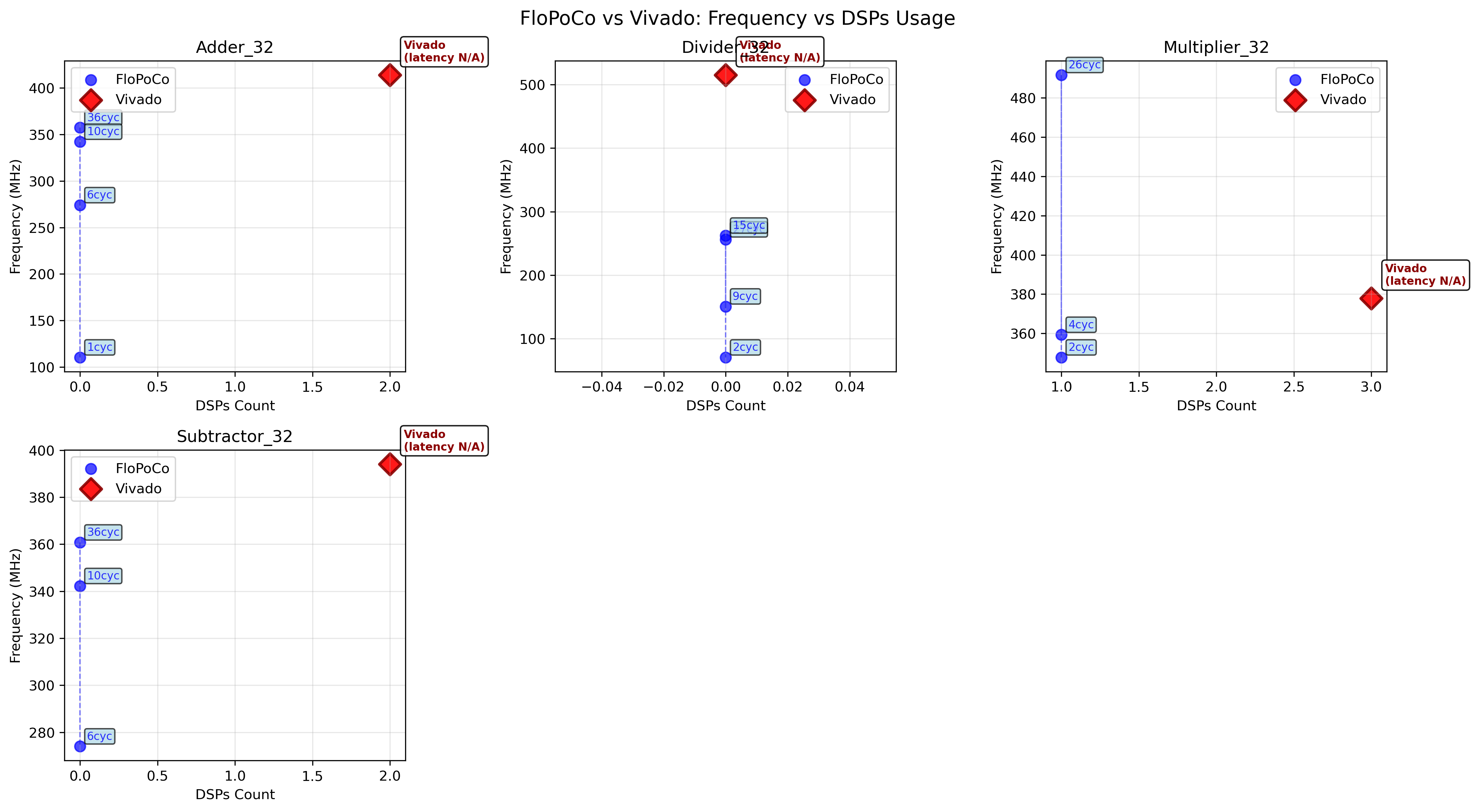
Performance comparison : FloPoCo vs Vivado
This section presents some reference side-by-side comparisons of operating frequency and ressource usage for common 32-bit operators, between FloPoCo and Vivado.. All the data presented was obtained by perfoming a place and route in Vivado 2019.1 and using the provided timing and utilsiation reports.